How Machine Translation Transcends International Boundaries in the Legal Industry
Machine translation has revolutionized the way we bridge language barriers in various sectors, with the legal industry being no exception. However, machine translation has been questioned if it can handle it due to the nature of law requiring precise wording and contextual nuances in translating legal text. The legal industry, often constrained by jargon-heavy language, faces the challenge of making legal documents, proceedings, and regulations accessible to a global audience.
For this reason, many courts don't accept machine-translated legal documents due to fear of inaccuracies or lack of legal context. Today, we will discuss how you can leverage machine translation for your legal documents and the best translation tools for it.
Challenges in Translation for the Legal Profession
The realm of legal translation is fraught with challenges, primarily due to the intricate nature of legal language and terminology. Below are some of the challenges that you should consider when translating legal documents with machine translation, as follows:
-
Complex Legal Terminology: Legal language's specialized terms, often without direct equivalents in other languages, pose a complex challenge for translators needing to convey precise legal concepts accurately across various legal systems.
-
Variations in Legal Systems: Global legal systems, each with distinct laws, regulations, and terminologies, present a challenge: a term in one system may differ or be absent in another, requiring translators to be linguistically adept and well-versed in these diverse legal frameworks for accurate translations.
-
Cultural Differences: Translators must skillfully navigate the cultural context and nuances of legal documents, ensuring translations are culturally relevant and sensitive to both the source and target audience's cultural subtleties.
-
Risk of Misinterpretation: In legal matters, where stakes are high, even minor translation errors can cause major repercussions, altering document meanings and potentially leading to disputes or misapplications of law, making absolute accuracy crucial.
-
Consistency and Uniformity: Translating legal texts requires consistent terminology and style throughout the document. This uniformity is crucial for the coherence and integrity of legal documents, especially in lengthy or multipart documents.
-
Confidentiality and Ethical Considerations: Legal documents often contain sensitive information. Maintaining confidentiality while translating such documents is a critical ethical obligation for legal translators. This adds a layer of responsibility to the already complex task.
Role of Machine Translation for the Legal Industry
Machine translation (MT) has become a crucial tool in addressing the complexities of translating legal content, offering significant aid in navigating the intricacies of legal language and terminology across various jurisdictions.
Powered by advanced algorithms and AI, machine translation is invaluable in legal contexts for quickly translating large volumes of documents like contracts, patents, and court filings. This rapid translation is crucial for legal teams dealing with the challenging task of reviewing thousands of documents in various languages, particularly during international litigation or corporate mergers. MT offers a fast, preliminary translation, aiding in identifying key documents for further detailed review or human verification.
However, the precision and subtleties of legal language require the cautious use of MT. Minor errors can lead to significant legal misunderstandings. The legal industry often employs a hybrid approach, integrating MT with human oversight to address this. This strategy proved effective in a significant European Union case, where legal experts meticulously revised initial machine translations, balancing efficiency and accuracy.
Recent advancements in machine learning have also led to the development of more sophisticated MT systems trained explicitly on legal datasets that are better equipped to handle the unique terminology and syntax found in different legal languages and systems, improving overall accuracy.
Advancements in Technology
Recent advancements in machine translation technologies, notably driven by artificial intelligence (AI), have significantly enhanced translation accuracy. The shift to neural machine translation (NMT) marks a pivotal change. NMT, unlike its rule-based and statistical predecessors, employs deep learning algorithms to process vast data sets, greatly improving translation quality and context sensitivity.
A notable development in this field is the creation of AI models adept at grasping and replicating human language nuances. These models are trained on extensive datasets, covering a range of languages, specialized terminologies, and legal jargon, enabling them to capture linguistic intricacies and provide contextually relevant translations accurately.
AI-driven translation tools now also feature adaptive learning, allowing them to learn from errors and user feedback for continuous performance enhancement. This aspect is particularly crucial in translations for legal settings, where accuracy is vital.
Integrating AI with technologies like Natural Language Processing (NLP) has resulted in more advanced translation tools. These tools can interpret complex sentence structures, idioms, and cultural nuances, effectively narrowing the language gap. These advancements speed up translation processes and elevate accuracy and contextual understanding, which are essential in various fields, especially in the detail-oriented realm of legal translation.
MT Benefits for the Legal Industry
Machine translation (MT) offers significant efficiency benefits in managing multilingual legal cases. Legal proceedings often require analyzing extensive documentation, and MT accelerates this process by quickly translating large volumes of text. This particular translation is vital in urgent situations like litigation or international negotiations, where prompt information access is critical.
Another significant advantage of MT is cost-effectiveness. Employing professional translators for substantial documentation in legal cases can be costly. MT is a cost-efficient alternative, significantly reducing financial strain on law firms and clients. While it doesn't completely replace the need for human translators, especially for critical documents, it considerably lowers overall translation expenses by managing most of the workload.
Scalability is a crucial feature of MT, particularly beneficial in international legal cases. MT systems can efficiently manage increasing workloads without proportional rises in cost or time, making them ideal for extensive, multilingual legal proceedings.
Additionally, it boosts legal service accessibility by enabling multilingual support in law firms and courts, enhancing non-native speakers' access to legal resources. This is crucial in international contexts, streamlining processes, reducing costs, and enhancing global legal effectiveness.
Limitations and Considerations
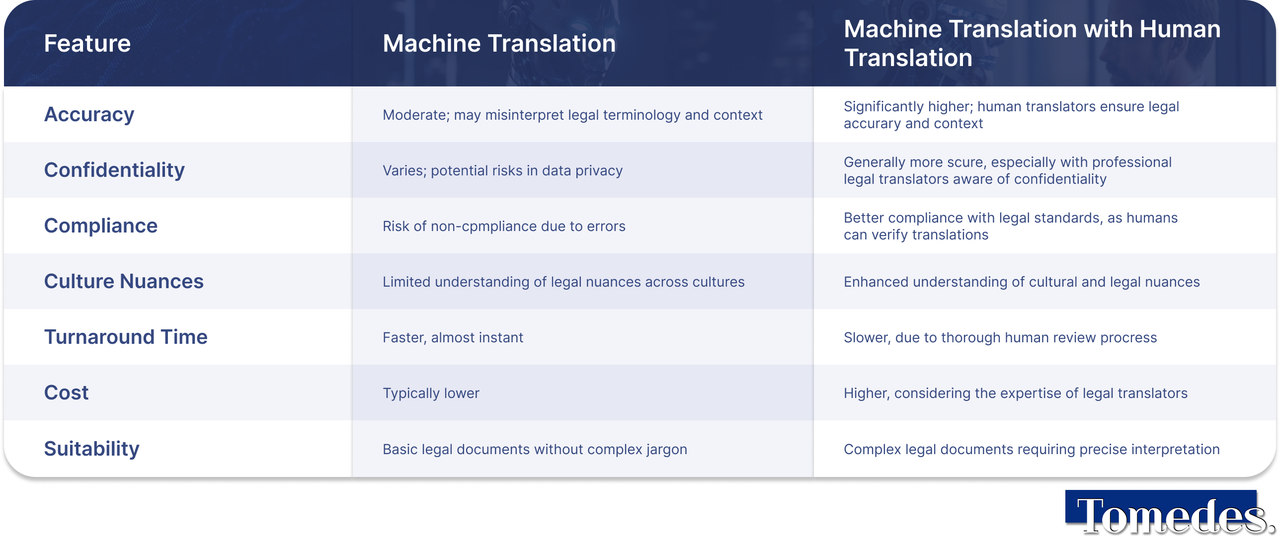
Despite advancements, machine translation (MT) faces significant challenges in legal translation, where precision and nuance are critical. Legal language, characterized by its complexity and specialized terminology, often needs more direct equivalents in other languages. Consequently, MT systems, despite their sophistication, may struggle with these nuances, risking significant legal misinterpretations.
Another issue is the contextual adaptation of legal texts across diverse legal systems and cultural practices. MT's ability to accurately reflect these differences is limited, which can lead to misunderstandings of legal principles and practices.
A hybrid approach is recommended to optimize MT in the legal context. This involves using MT in the legal context, such as drafts or large text volumes, followed by legal translators reviewing and refining it. This strategy combines MT's efficiency with human expertise's accuracy and contextual sensitivity.
Improving machine translation accuracy requires frequent updates and customizations for specific legal terms and contexts. Educating legal professionals on its strengths and limitations is vital for its appropriate, practical use, necessitating a cautious, informed approach in the legal industry.
FAQs
What are the steps to integrate machine translation into a legal firm's workflow?
To integrate machine translation into your legal firm's workflow, follow these steps:
Assessment: Evaluate the types of documents and translation needs.
Tool Selection: Choose a machine translation tool tailored for legal content, ensuring it supports your required languages.
Integration: Implement the tool within your existing document management system.
Training: Train staff on using the machine translation tool effectively.
Quality Control: Establish a process for reviewing and editing translations to ensure accuracy and compliance.
Feedback Loop: Regularly review performance and provide feedback to improve translation quality over time.
What are the cost implications of using machine translation compared to human translators in the legal industry?
Using machine translation can significantly reduce costs compared to human translators. Machine translation tools often have subscription-based pricing, which can be more economical for high-volume translation needs. While the initial setup and integration might incur some costs, the long-term savings on translation fees are substantial. However, for critical documents, you might still need human translators to ensure precision and legal compliance, adding to the cost. Balancing machine translation with human oversight can optimize both cost and quality.
What are the potential legal liabilities of using machine-translated documents in court or legal proceedings?
Using machine-translated documents in court or legal proceedings can pose several legal liabilities. Inaccurate translations may lead to misinterpretations, affecting the case outcome. Courts might question the credibility of machine-translated documents, leading to their rejection. Additionally, errors in translation could result in non-compliance with legal standards and potential legal repercussions. To mitigate these risks, it's crucial to have machine translations reviewed and certified by professional human translators, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the documents used in legal contexts.
Conclusion
Machine translation revolutionizes the legal industry's efficiency, affordability, and scalability, notably in managing vast legal documents and aiding international proceedings. Advanced technologies like AI-driven neural machine translation significantly improve accuracy and contextual understanding in translations.
Legal language's nuances and the diversity of global legal systems demand a hybrid MT approach, blending technology's speed with human precision. Continuous updates and training are crucial for MT's effectiveness in legal contexts. As we advance in this digital era, legal professionals must embrace and adapt to these technological innovations, leveraging them to enhance the global practice of law.

By Clarriza Heruela
Clarriza Mae Heruela graduated from the University of the Philippines Mindanao with a Bachelor of Arts degree in English, majoring in Creative Writing. Her experience from growing up in a multilingually diverse household has influenced her career and writing style. She is still exploring her writing path and is always on the lookout for interesting topics that pique her interest.
Share:
GET IN TOUCH
Need expert language assistance? Inquire now
Try free AI tools to streamline transcription, translation, analysis, and more.
Use Free Tools
Post your Comment